মাটির উপর ভিত্তি করে শিল্পীকৃত পুনঃচক্রবদ্ধ জলজ চাষ পদ্ধতি (RAS) প্রক্রিয়া এবং প্যারামিটার ডিজাইন (অংশ ১)
প্রক্রিয়া ডিজাইন
ভূমি-ভিত্তিক শিল্পীকৃত পুনঃচক্রবদ্ধ জলজ চাষ পদ্ধতি (RAS) (RAS)
ভূমি-ভিত্তিক শিল্পীকৃত পুনঃচক্রবদ্ধ জলজ চাষ পদ্ধতি (RAS) (RAS) আধুনিক শিল্পীকৃত প্রযুক্তি—যেমন প্রকৌশল, জীববিজ্ঞান, যান্ত্রিক সরঞ্জাম, তথ্য পদ্ধতি, এবং বৈজ্ঞানিক পরিচালন—এর উপর নির্ভর করে জলজ প্রাণী চাষের প্রক্রিয়াটি সম্পূর্ণভাবে নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে। এটি জলজ প্রাণীদের জন্য অপ্টিমাল পরিবেশগত শর্তগুলি তৈরি করে, যাতে সাল দীর্ঘ উচ্চ ঘনত্বের, উচ্চ কার্যকারিতার এবং স্বাস্থ্যকর উৎপাদন সম্ভব হয় , এবং মাছের পালনের ভবিষ্যতের জন্য একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ দিক নির্দেশ করে।
ডিজাইন ফ্লো
ডিজাইনটি পুনঃচক্রবদ্ধ জলজ চাষ পদ্ধতি (RAS) জল প্রসেসিং প্রক্রিয়া ভিত্তিক মাতেরিয়াল ব্যালেন্স তত্ত্ব , মূল উদ্দেশ্য হল দ্রুত ক্ষতিকারক পদার্থ (যেমন, টাঙ্গানো কণাবিশিষ্ট, অ্যামোনিয়া নাইট্রোজেন) সরিয়ে ফেলা। এই দূষণের জন্য ব্যালেন্স সমীকরণ স্থাপন করা হয় সিস্টেম প্যারামিটার নির্ধারণের জন্য, যা তারপরে ব্যবহার করে সুনির্দিষ্ট করা হয় ইঞ্জিনিয়ারিং বাস্তব অভিজ্ঞতা মডেলের নির্ভরশীলতা বাড়াতে।
প্রধান ডিজাইন প্যারামিটারগুলি নির্ভর করে: পালিত প্রজাতি এবং সর্বোচ্চ জৈব ভার বহন ক্ষমতা (জৈব ভার বহন ক্ষমতা = ঘনতা) × কার্যকর জলের আয়তন ) এরপর দৈনিক খাদ্য ইনপুট এবং মোট অপচয় (ঠিকানা কণা, অ্যামোনিয়া নাইট্রোজেন) গণনা করা হয়। এই মানগুলি সরঞ্জামের প্রকাশ (যেমন, বায়োফিল্টারের আকার, বায়ো-মিডিয়া আয়তন, মাইক্রোস্ক্রীন ফিল্টার ক্ষমতা) নির্ধারণ করে।
ধাপে ধাপে কাজের ফ্লো
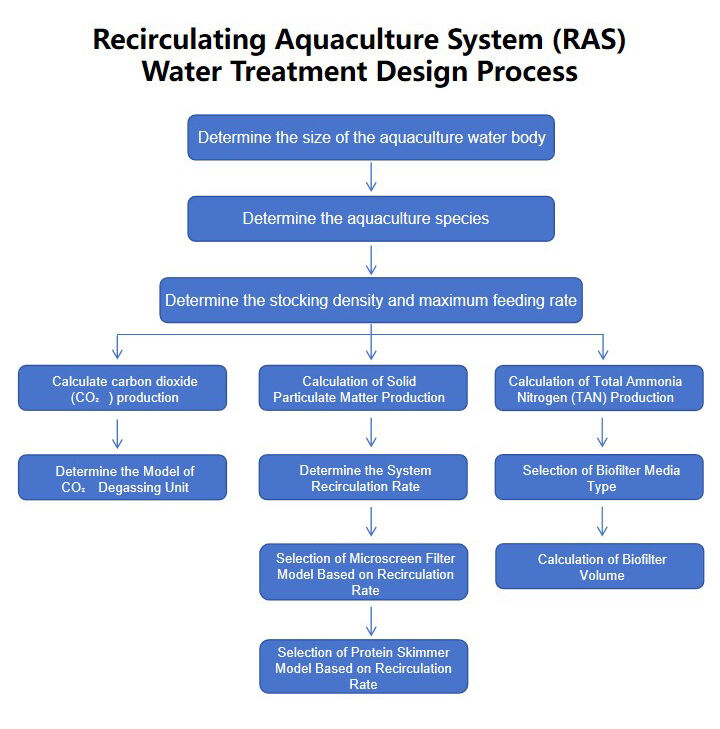
ধাপ ১: জলজ প্রাণী চাষের জলের আয়তন নির্ধারণ করুন
জলের আয়তন নির্ধারণ করতে হবে ভিত্তিতে জমির উপলব্ধি, আর্থিক ক্ষমতা এবং চালু কর্মকান্ডের স্কেল উন্নয়ন।
ধাপ ২: জলজ প্রাণী চাষের প্রজাতি নির্বাচন করুন
প্রজাতি নির্বাচনের সময় বিবেচনা করতে হবে: জলের গুণবাত সঙ্গতি , কৃষি জটিলতা, উৎপাদন চক্র, বাজার চাহিদা, অর্থনৈতিক সম্ভাব্যতা।
ধাপ 3: স্টকিং ঘনত্ব এবং সর্বোচ্চ দৈনিক খাদ্য ইনপুট নির্ধারণ করুন
নির্বাচিত প্রজনন প্রজাতি এবং প্রজননের জল শরীরের আকারের উপর ভিত্তি করে একটি যৌক্তিক প্রজনন ঘনত্ব গণনা করুন এবং এটি ব্যবহার করে সর্বোচ্চ দৈনিক খাদ্য পরিমাণ গণনা করুন।
ধাপ 4: সর্বোচ্চ অপশিষ্ট উৎপাদন পরিমাপ করুন
একীভূত পরিবর্তনশীল জল প্রক্রিয়া ডিজাইনের মূল বিষয় হল খাদ্য দেওয়ার পর উৎপাদিত প্রজনন অপশিষ্টকে কিভাবে দ্রুত সরানো যায়। অন্য কথায়, খাদ্য দেওয়ার আগে জলজ পুকুরের সমস্ত জল পরিমাপ সূচক সমদ্বিমূলক এবং মানদণ্ড মেনে চলে। কিন্তু বিশাল পরিমাণে খাদ্য ঢালার পর প্রজনন পুকুরের সুষমতা বিক্ষিপ্ত হয় এবং বিশাল পরিমাণে ঠক্কা, তরল এবং গ্যাস অবস্থার অপশিষ্ট উৎপন্ন হয়।
ধাপ 5: জল প্রক্রিয়া সরঞ্জাম ডিজাইন করুন
অপশিষ্টের সর্বোচ্চ মোট পরিমাণের উপর ভিত্তি করে জল প্রক্রিয়া সরঞ্জামের পারফরমেন্স প্যারামিটার গণনা করুন .
তথ্য প্রক্রিয়া পরামিতি
|
তথ্য প্রক্রিয়া পরামিতি |
|
|
পুনঃপ্রবাহকারী জল প্রणালীর সর্বোচ্চ চক্র সংখ্যা |
24চক্র/দিন |
|
প্রজনন ঘনত্ব |
সামুদ্রিক জল (উদাহরণ: গ্রুপার): ≥50 কেজি/ম³ শুষ্ক জল (উদাহরণ: বাস): ≥50 কেজি/ম³ |
|
পুনঃ ব্যবহারযোগ্য জলের ব্যবহারের হার সরকুলেটিং জল পদ্ধতিতে |
≥90% |
|
জল বিনিময়ের হার |
≤১০% |
|
ইউভি দ্বারা শোষণের হার |
≥99.9% |
বিশেষ কার্যক্রমের মোড
সাধারণ জলজীবন মোডের বাইরেও, প্রক্রিয়ার সময় নিম্নলিখিত সাধারণ উপাদানগুলিও বিবেচনা করা উচিত পুনর্প্রবাহী জলজ প্রাণী চাষ (RAS) সিস্টেম (RAS) .
১. বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদের আপাতকালীন মোড
জলজ প্রাণী চাষের প্রক্রিয়ার মধ্যে বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদ ঘটলে পুনর্প্রবাহী জল চাষ সিস্টেমে গুরুতর ক্ষতি ঘটতে পারে, তাই ডিজাইনে বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদের জন্য একটি আপাতকালীন মোড থাকা প্রয়োজন যা বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদের ঝুঁকি থেকে রক্ষা করবে।
১) পশ্চাত্তাপী জেনারেটর ইনস্টল করুন: বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদের ক্ষেত্রে জেনারেটরটি দ্রুত চালু করুন যাতে পুনর্প্রবাহী জল প্রणালীর সাধারণ কার্যকারিতা নিশ্চিত থাকে।
২) অতিরিক্ত জল নির্গম পাইপলাইন ডিজাইন করুন: যখন পাম্পটি বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদে কাজ করছে না, তখন অতিরিক্ত জল নির্গম পাইপলাইন জল পাম্প থেকে দ্রুত নির্গত করতে সহায়তা করবে যাতে জল পাম্প থেকে বাহির হওয়া বন্ধ থাকে।
৩) আপাতকালীন অক্সিজেন সরবরাহ সংযুক্ত করুন: নিম্ন দিষ্ট অক্সিজেনের শর্তে চাষের প্রাণীগুলি দ্রুত মারা যেতে পারে। তরল অক্সিজেন পদ্ধতি বিদ্যুৎ নির্ভরশীল নয় এবং বিদ্যুৎ বিচ্ছেদের সময় চাষের ডিঙ্গিতে অক্সিজেন সরবরাহ করতে পারে যা চাষের প্রাণীদের সংরক্ষণে সাহায্য করে।
অন্তিষ্টক মোড
শুধুমাত্র পদার্থগত স্টেরিলাইজেশনের উপর নির্ভর করে জলকে স্বচ্ছ করা যথেষ্ট নয় যদি প্রজননের সময় প্রজননশীল প্রাণীরা রোগ উন্মুক্ত হয়। এই সময়ে, কিছু রাসায়নিক ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে স্বচ্ছতা ও স্টেরিলাইজেশনের জন্য। রাসায়নিক ঔষধির অবশিষ্টাংশ জল পরিচালনার মাধ্যমে বায়ো-কেমিক্যাল ফিল্টারে প্রবেশ করতে পারে। বায়ো-কেমিক্যাল ফিল্টারের নাইট্রোফাইন্গ ব্যাকটেরিয়া খুবই সংবেদনশীল। রাসায়নিক দ্রব্যের প্রবেশ বড় আকারে নাইট্রোফাইন্গ ব্যাকটেরিয়াকে হত্যা করতে পারে। সুতরাং, ডিজাইন করার সময় একটি পুনঃচক্রবদ্ধ জলজ চাষ পদ্ধতি (RAS) সিস্টেমের জন্য, একটি আলাদা স্বচ্ছতা মোড থাকতে হবে। যখন রাসায়নিক স্বচ্ছতা প্রয়োজন, তখন নিশ্চিত করুন যে পরিচালিত জল বায়ো-কেমিক্যাল ফিল্টার দিয়ে প্রবাহিত না হয়।
আইডল মোড
চামড়া পরিবেশে, ভ্যালভের ধাতব উপাদানগুলি (যেমন ভ্যালভ স্টেম, ভ্যালভ কোর ইত্যাদি) বায়ুতে অক্সিজেন এবং নির্যাসের সাথে রাসায়নিক বিক্রিয়ার ঝুঁকির মুখোমুখি হয়, যা ফলে আঁটি গঠন ঘটায়। উৎপাদন প্রক্রিয়ার সময়, ভ্যালভ অনেক সময় ঘূর্ণন করে এবং উপাদানের মধ্যে ঘসে চলার ফলে আঁটি দূর হয়। তবে, দীর্ঘ সময়ের জন্য রক্ষণাবেক্ষণের ফলে ভ্যালভের উপাদানের মধ্যে বেশি পরিমাণে আঁটি জমা পড়তে পারে, ভ্যালভের উপাদানের মধ্যে ঘষন বৃদ্ধি পায় এবং ভ্যালভের ঘূর্ণন বা খোলার সমস্যা তৈরি করতে পারে। এই কারণে, রক্ষণাবেক্ষণের মোডে, সকল ভ্যালভকে প্রতিদিন একবার খোলা হয় যাতে দীর্ঘ সময়ের জন্য ব্যবহার না করার কারণে ভ্যালভের ত্রুটি ঘটে না।
উপরের বিশেষ মোডের দেওয়া হিসেবে, যদি মনে করা হয় যে এই কাজটি তুলনামূলকভাবে জটিল, তবে শ্রমিকদের ভুল করলে অপ্রয়োজনীয় ক্ষতি ঘটতে পারে। ব্যাং ব্যাং সংস্থাটি বিভিন্ন পরিস্থিতির জন্য ভিন্ন ভিন্ন চালনা মোডে সুইচ করতে পারে এমন একটি চক্রের জলের জন্য চালিত স্মার্ট নিয়ন্ত্রণ পদ্ধতি চালু করেছে।
প্রস্তাবিত পণ্য
উত্তপ্ত খবর
-
কানভাস মৎস্য ডাঙা ব্যবহার করে মাছ পালন করা সাধারণ ডাঙার তুলনায় কি বেশি কার্যকর?
2024-12-16
-
গ্যালভানাইজড ক্যানভাস মাছের তালাবের সুবিধাগুলি
2024-10-14
-
উচ্চ ঘনত্বের মাছ চাষের প্রযুক্তি, মাছের তালাবের খরচ, ক্যানভাস মাছের তালাব, ক্যানভাস তালাব, উচ্চ ঘনত্বের মাছ চাষ
2024-10-12
-
কেন প্রবাহিত জলে উচ্চ ঘনত্বের একুশ নির্বাচন করুন
2023-11-20